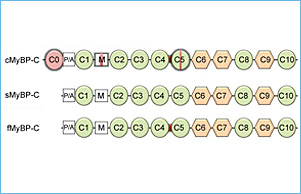
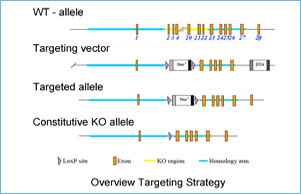
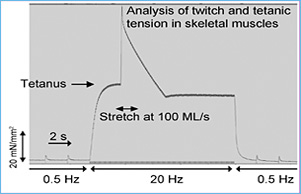
Myosin binding protein-C (MyBP-C) consists of fast skeletal (fMyBP-C), slow skeletal (sMyBP-C), and cardiac isoforms (cMyBP-C). Both cMyBP-C and sMyBP-C have been demonstrated to be necessary for normal striated muscle function, and they are important regulators of actin-myosin interactions. However, the precise function of fMyBP-C is unknown, and its role in skeletal muscle remains enigmatic. Thus, this project will characterize the regulatory roles of sMyBP-C in skeletal muscle in health and disease. Despite their names, fast and slow isoforms of MyBP-C are not exclusively expressed in fast-twitch or slow-twitch skeletal muscles. Rather, they are coexpressed in varying ratios, and each may have distinct functions. Therefore, understanding how sMyBP-C regulates muscle contraction at the cellular and molecular level is particularly important in the context of muscle disease, which is often characterized by muscle weakness and impaired function.
Sakthivel Sadayappan, PhD, MBA, FAHA
Professor and Head
Department of Cellular & Molecular Medicine
Associate Director, Sarver Heart Center
Czarina M. & Humberto S. Lopez Chair for Excellence in Cardiovascular Research
University of Arizona College of Medicine
Tucson, AZ 85724-5217, USA